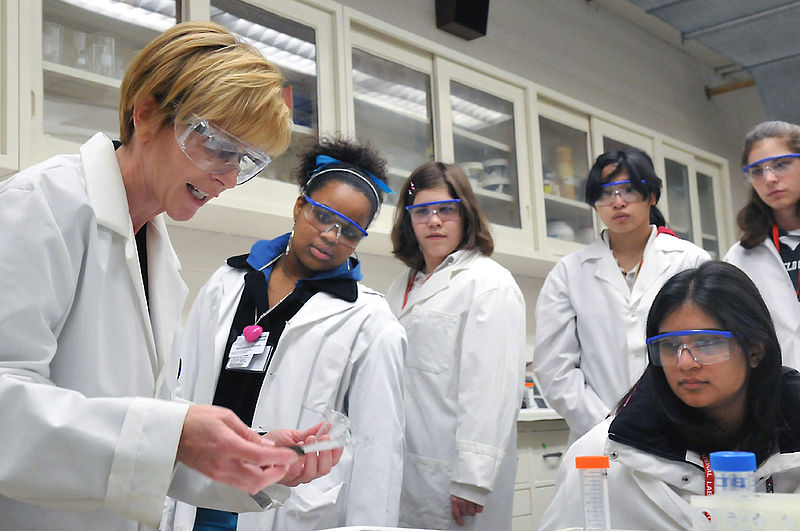
Economists around the world emphasize the benefits of integrating more women into the workforce. While we are seeing slow growth in women’s presence in many sectors, the Science, Technology, Engineering, and Math (STEM) fields at the core of innovation seem to be especially lacking in girl power.
In 2014, women comprised approximately 47 percent of the U.S. workforce. Within the innovation-focused STEM fields, women only account for about 19.5 percent. This underrepresentation of women is not only holding women back from success and achieving their full potential, but also preventing the U.S. economy from realizing the wide array of benefits which come from increasing women’s labor force participation.
Why We Need More Women in STEM
When women get involved in STEM fields, they are rewarded. Compared to similar women who are working in non-STEM fields, the salaries of women in STEM are 33 percent higher. For men, the difference is only 25 percent. Not only are salaries higher, but the gender pay gap is also smaller. A 2011 U.S. Department of Commerce study found that the average gap is 21 percent in non-STEM jobs. For STEM jobs, this gap is only 14 percent.
Women aren’t the only ones who benefit. Companies that place an emphasis on gender equality and hiring women tend to see positive impacts on their productivity and success. For companies marketing to women, the Harvard Business Review has shown that having input from women improves their “likelihood of success” by 144 percent. Innovative firms, along with many traditional businesses, can benefit from having female perspectives to help reach female customers.
Gender diversity in the workplace also enhances creativity among workers. When researchers at the University of Maryland and Columbia University teamed up to study top leadership in Standard and Poor’s Composite 1500 list, they found that female representation in leadership positions is associated with a $42 million increase in average firm value. They also saw that companies which emphasized innovation received higher financial gains when women were in top management.
U.S. Initiatives to Empower STEM Women
The Obama Administration has made efforts to increase women’s involvement in STEM. In 2009, President Barack Obama created the White House Council on Women and Girls, a team that coordinates U.S. policy, legislation, and programs to address the needs of women and girls. The Council has made women’s involvement in STEM a particular priority. They have announced multiple initiatives, like Title IX protections for equal education, work-life balance programs, and speaking tours for successful women innovators. The administration also made efforts to eliminate the gender pay gap through the creation of an Equal Pay Task Force in 2010 and an executive order affecting federal contractors in 2014.

These actions alone cannot address the full extent of gender inequality. However, they may improve the situation. Policies that encourage girls to explore their interest in STEM give girls the opportunity to develop passions in these fields. Once these passions become careers, flexible and non-discriminatory policies in the workplace can incentivize women to stay involved in STEM throughout their careers.
Women in STEM around the World
In North America and Western Europe, on average, only 32 percent of researchers, defined as “professionals engaged in the conception or creation of new knowledge, products, processes, methods and systems and also in the management of the projects concerned,” are women. Japan, one of the leading tech development nations, has a mere 15 percent. Surprisingly, Central Asia has the highest average proportion of women researchers, with 47 percent.
The United Kingdom ranks second in world scientific achie vement, behind the United States. 35.7 percent of researchers in the UK are women. Within solely STEM fields, though, the proportion of women is even lower: only 14.4 percent. This trend is apparent across many of the nations with the highest investments and achievements in STEM.
vement, behind the United States. 35.7 percent of researchers in the UK are women. Within solely STEM fields, though, the proportion of women is even lower: only 14.4 percent. This trend is apparent across many of the nations with the highest investments and achievements in STEM.
Differences in gender norms affect incentives for women to enter these fields. In some regions, like India, women are expected to be caretakers and homemakers. Their participation in STEM, and the workforce in general, is therefore often very low. On the other end of the spectrum, there are certain areas in Asia where gender stereotypes regarding math and science are less prevalent. In these areas, STEM interest is greater among women than men.
Culture clearly has an effect on the proportion of women who get involved in STEM professions. A prevailing stereotype exists in American society that women are inferior to men in math and science. Although this stereotype has been proven untrue, societal beliefs and expectations can have an effect on women’s empowerment. Research by Claude M. Steele shows the effects of stereotypes on performance and self-perception. If we want to see a change in the proportion of women in STEM, we need to change our culture.
What is the Future for Women in STEM?
Remedying the gender gap in innovation fields is not a simple or quick process. It requires a combination of education for girls, policy changes that eliminate barriers for women workers, cultural changes, shifts in societal prioritization of gender equality, and much else besides. At the current progress rate, we are a long way from eliminating the gender gap. However, with concerted effort from policymakers, educators, and employers, there is hope for a fairer and more productive future.



 Andrew Maust joined the team last spring after going to several tea tastings. Since then, he’s climbed the ladder from kitchen worker to operations manager.
Andrew Maust joined the team last spring after going to several tea tastings. Since then, he’s climbed the ladder from kitchen worker to operations manager.



 On December 1, 2016, the Labor Department will officially institute new regulations on overtime eligibility for workers. Announced on May 17, the
On December 1, 2016, the Labor Department will officially institute new regulations on overtime eligibility for workers. Announced on May 17, the 
 The doctor-patient relationship is an important aspect of healthcare. Small physician practices, offices with no more than a couple doctors, have been the long-standing foundation of this relationship. Unfortunately, legislative changes disincentivize doctors from being small business owners.
The doctor-patient relationship is an important aspect of healthcare. Small physician practices, offices with no more than a couple doctors, have been the long-standing foundation of this relationship. Unfortunately, legislative changes disincentivize doctors from being small business owners.
 4.1% each.
4.1% each.


